Inner Alliance
Inner Alliance is a tabletop turn-based tactical rescue game where players lead a team of specialists through a flooded environment in a top-down, XCOM-style format. Beyond promoting strategy and teamwork, it serves as an educational tool to foster diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) within military organizations. By leveraging interactive media, the game engages players in complex decision-making, emphasizing the importance of inclusive collaboration in high-stakes scenarios.
I joined the project through the Archipelago of Design to transform the board game into a video game, taking on the full scope of programming. The team later grew to include talented designers and artists, enhancing the project’s development, which remains ongoing with promising progress.
Hex Grid Implementation
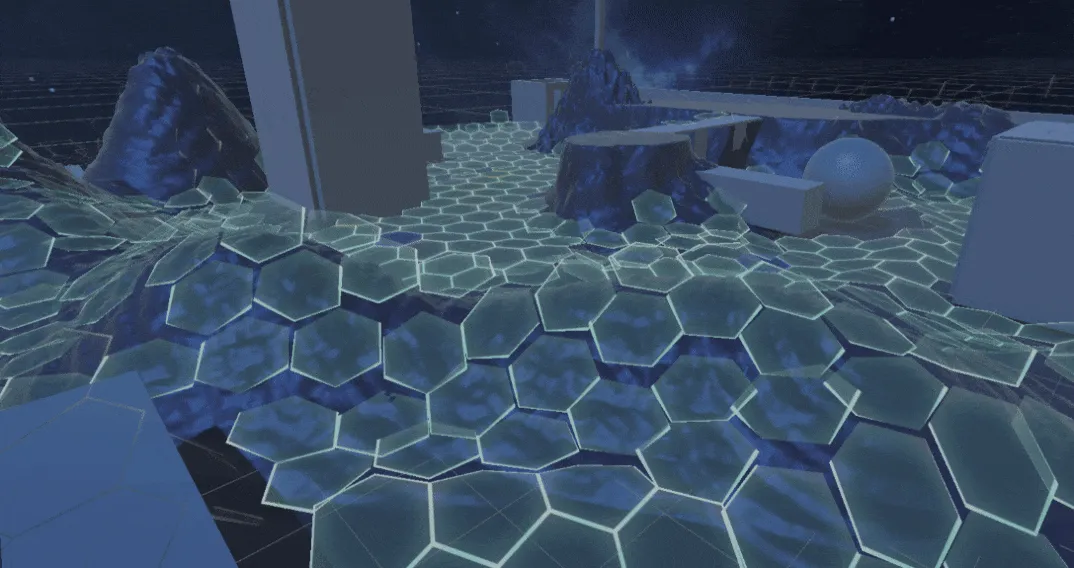
Hex grids are popular in strategy games for their flexible movement and natural pathing—making them a great fit for Inner Alliance’s tactical gameplay. We built our system on Catlike Coding’s hex map tutorials and adapted it to suit our game’s specific needs.
- Data-Oriented Design: Hex data is stored in tightly packed structs for improved performance and cache efficiency.
- Flexible Mesh Generation: Modified to support various map shapes, like rectangular, circular, or hexagonal grids.
- Centered Coordinate System: Shifted the origin to
Coords(0, 0)at the map’s center, simplifying calculations compared to a bottom-left origin.
The RedBlobGames guide on hex coordinates was invaluable for mastering axial coordinates and conversions between systems.
Hex Challenges
Generating the hex grid posed challenges, especially with indexing and raycasting. The hexes are stored in an array, but raycasting returns a mesh position, not a hex. Converting this position to a hex coordinate is straightforward, but mapping it to the correct HexCell array index—determined by generation order—proved trickier.
To solve this, I introduced an IHexGridStrategy interface to handle generation and indexing logic for different map shapes (e.g., square, circular, or hex-shaped). This abstraction keeps the core hex grid code unchanged while supporting varied layouts. However, perfecting the algorithms was tough:
- Rectangular grids required offsetting positions and coordinates every other row due to their zigzag alignment.
- Ensuring internal coordinates matched the generated shape often revealed mismatches, demanding meticulous debugging.
Aligning the Hex Grid with Voxelization
Rather than crafting the hex grid in isolation, we align it to an existing environment, decoupling the visual scene from the gameplay map for a streamlined workflow.
Initially, I used a simple raycasting method—projecting rays downward from each hex to match the environment’s positions and normals. This worked for flat surfaces but faltered on varied terrain, where accuracy suffered. Increasing raycasts per hex (e.g., six) improved results marginally but hurt performance.
Switching to a voxelization approach, inspired by Unity’s nav mesh techniques (see this and this), proved more effective:
- Scene Analysis: Identify all meshes and terrains, combining their bounds into a single volume.
- Voxel Creation: Generate a 3D grid of boolean voxels covering the bounds.
- Intersection Detection: Enable voxels intersecting any mesh or terrain (visualized as green).
- Hex Placement: Position each hex on the nearest enabled voxel, adjusting rotation to align with surrounding voxel normals.
Voxel Challenges
Implementation wasn’t without hurdles:
Vertex Intersection Errors: Early voxelization only detected mesh edges, missing interiors. Applying the Separating Axis Theorem fixed this by properly testing voxel-triangle intersections.
Hex Normal Calculation: Averaging neighbor normals often failed near cliffs, leaving hexes tilted or overhanging. Reducing neighbor range didn’t help, but weighting each neighbor’s influence inversely by distance smoothed transitions and kept hexes level.